Leveraged ETFs Explained: A Double-Edged Sword
What every trader and investor should know about these high-octane funds.
Hi everyone! With the markets closed today for a national day of mourning to honor President Jimmy Carter, I thought this would be a perfect moment to dive into a topic I’ve been meaning to discuss for a while: leveraged ETFs.
Leveraged ETFs can be powerful tools for traders, but like all things in life—and especially in trading—they come with their own risks and rewards. Whether you're curious about how these funds work, considering them as part of your strategy, or simply want to sharpen your knowledge, this article is for you. Let’s break it down together.
What Are Leveraged ETFs?
Leveraged ETFs aim to deliver a multiple of the daily performance of an underlying index. For example:
A 2x Leveraged ETF seeks to return twice the daily movement of an index (e.g., S&P 500).
A 3x Leveraged ETF seeks three times the daily movement.
In addition to "bull" leveraged ETFs, which magnify gains in the direction of the index, there are also inverse leveraged ETFs designed to profit from the index's decline.
These ETFs achieve leverage through derivatives such as futures contracts, options, and swaps. Unlike traditional ETFs, which passively track an index, leveraged ETFs reset daily, recalculating their leverage to reflect the index’s daily returns.
Why Use Leveraged ETFs?
Short-Term Speculation: Leveraged ETFs are popular among traders looking to profit from short-term market movements.
Hedging: Inverse leveraged ETFs provide a way to protect a portfolio during market downturns.
Amplifying Returns: They enable traders to achieve higher returns with less capital compared to directly trading futures or margin accounts.
Understanding the Risks
While the potential for higher returns is appealing, the risks of leveraged ETFs are significant:
1. Compounding Effects
Leveraged ETFs reset daily, which can lead to unexpected results over time. For example, in a volatile market, the compounding of daily returns can cause the ETF’s performance to deviate significantly from the underlying index’s long-term return.
Example: Suppose an index rises by 5% one day and falls by 5% the next. Over two days, the index returns -0.25%. A 2x leveraged ETF would lose more due to the amplified daily movements, resulting in greater losses.
2. Volatility Decay
In sideways or choppy markets, leveraged ETFs often lose value even if the index price remains flat over time. This phenomenon, known as "volatility decay," makes these ETFs less effective for buy-and-hold strategies.
3. Higher Costs
Leveraged ETFs typically have higher expense ratios (often 0.5% to 1%) compared to standard ETFs, reflecting the cost of derivatives and leverage.
4. Not for Long-Term Holding
Holding leveraged ETFs over weeks or months can produce unpredictable returns, often far different from what an investor might expect based on the index’s overall performance.
Performance Examples
To illustrate, consider the following scenario:
Despite the index ending close to break-even, the leveraged ETFs underperform due to compounding effects.
Who Should Use Leveraged ETFs?
Day Traders: Those who closely monitor markets and want to amplify intraday returns.
Hedgers: Investors who use inverse leveraged ETFs to protect portfolios from short-term downside risks.
Sophisticated Investors: Traders with a deep understanding of leverage and the risks of compounding.
Key Considerations for Leveraged ETFs
1. Know the Index
Understand the underlying index and its behavior. Leveraged ETFs work best in trending markets with minimal volatility.
2. Monitor Volatility
Higher market volatility increases the likelihood of performance deviation. Use tools like the VIX to gauge risk levels.
3. Avoid Long-Term Holdings
Use these products for short-term strategies, as holding them for weeks or months often leads to disappointing results.
4. Understand Costs
Check the ETF’s expense ratio and daily reset mechanism to ensure you’re comfortable with the costs.
Popular Leveraged ETFs
Here’s an overview of popular leveraged ETFs that attract traders:
1. SOXL (Direxion Daily Semiconductor Bull 3x Shares)
Focus: Tracks 3x the daily performance of the PHLX Semiconductor Index.
Why It’s Popular: The semiconductor industry is highly cyclical and prone to sharp rallies. SOXL offers a way to capitalize on these movements with amplified exposure.
Risks: High volatility in the semiconductor sector can magnify losses during market downturns.
2. TSLL (Direxion Daily TSLA Bull 1.5x Shares)
Focus: Amplifies daily exposure to Tesla’s stock by 1.5x.
Why It’s Popular: Tesla is a high-growth, high-volatility stock, attracting speculative traders who want to capture big moves in either direction.
Risks: Tesla’s stock can experience significant volatility, making TSLL risky during drawdowns.
3. NVDL (Direxion Daily NVIDIA Bull 2x Shares)
Focus: Delivers 2x the daily performance of NVIDIA stock.
Why It’s Popular: NVIDIA’s role in AI, gaming, and data centers has made it one of the hottest stocks. Traders use NVDL to ride the AI boom.
Risks: NVIDIA’s valuation and sector-specific risks can lead to sharp declines.
4. MSTX (Direxion Daily MicroStrategy Bull 2X Shares)
Focus: The fund seeks to achieve 2x (200%) the daily percentage change in the share price of MicroStrategy Inc. (MSTR). It uses swap agreements with financial institutions to deliver this leveraged exposure.
Why It’s Popular: MicroStrategy (MSTR) is highly correlated to Bitcoin due to its significant Bitcoin holdings. MSTX offers traders a way to amplify gains on MSTR’s price movements without directly trading the stock or cryptocurrency. It appeals to those looking to capitalize on short-term trends in Bitcoin and MSTR’s stock price.
Risks:
As with all leveraged ETFs, MSTX is highly sensitive to volatility and compounding effects, especially in a choppy market.
The fund's focus on MicroStrategy’s price movements ties its performance closely to Bitcoin's price swings, adding another layer of volatility.
This ETF is non-diversified, making it inherently riskier than broader ETFs.
5. TQQQ (ProShares UltraPro QQQ)
Focus: Tracks 3x the daily performance of the Nasdaq-100 Index.
Why It’s Popular: The Nasdaq-100 is tech-heavy and known for rapid rallies during bull markets, making TQQQ a favorite for aggressive traders.
Risks: Tech stocks are highly volatile, and during downturns, TQQQ can suffer significant losses.
Conclusion: A Double-Edged Tool
Leveraged ETFs are a powerful but risky investment tool. They are best suited for experienced investors who can manage short-term strategies and understand the compounding and volatility risks. For long-term investors or those without a clear short-term strategy, traditional ETFs or other instruments may be more appropriate.
When used wisely, leveraged ETFs can enhance returns and hedge risks. But misusing them can lead to unexpected losses. Understanding their mechanics, risks, and appropriate use cases is the key to navigating the leveraged ETF landscape. As always, thank you for being part of this journey with me. I’ll continue working to bring you content that sharpens your trading edge and builds your confidence in the markets.
Until tomorrow, stay disciplined, stay profitable, and trade smarter! 🎯-EC
*Disclaimer The examples and information in this article are for educational purposes only and not financial advice
Looking For More Trade Ideas? Follow Me on Twitter/X EdwardCoronaUSA


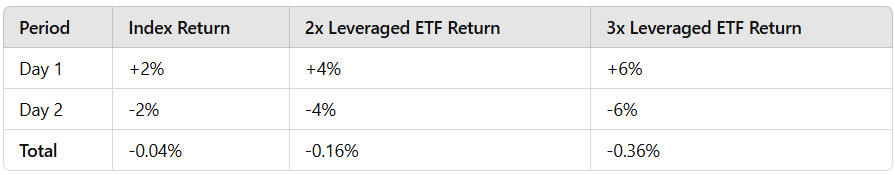
It's the down side on leveraged ETFs which is the least understood aspect by many. Good one!